Induction heating
Induction heating is an efficient, fast, non-contact, flame-free heating method commonly used to heat metallic materials. This process is based on electric currents induced in materials in order to produce heat. The technique also lends itself to several other applications involving packaging and polymerisation. Michael Faraday discovered the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction in 1831 and its use is widespread in today’s modern manufacturing processes.
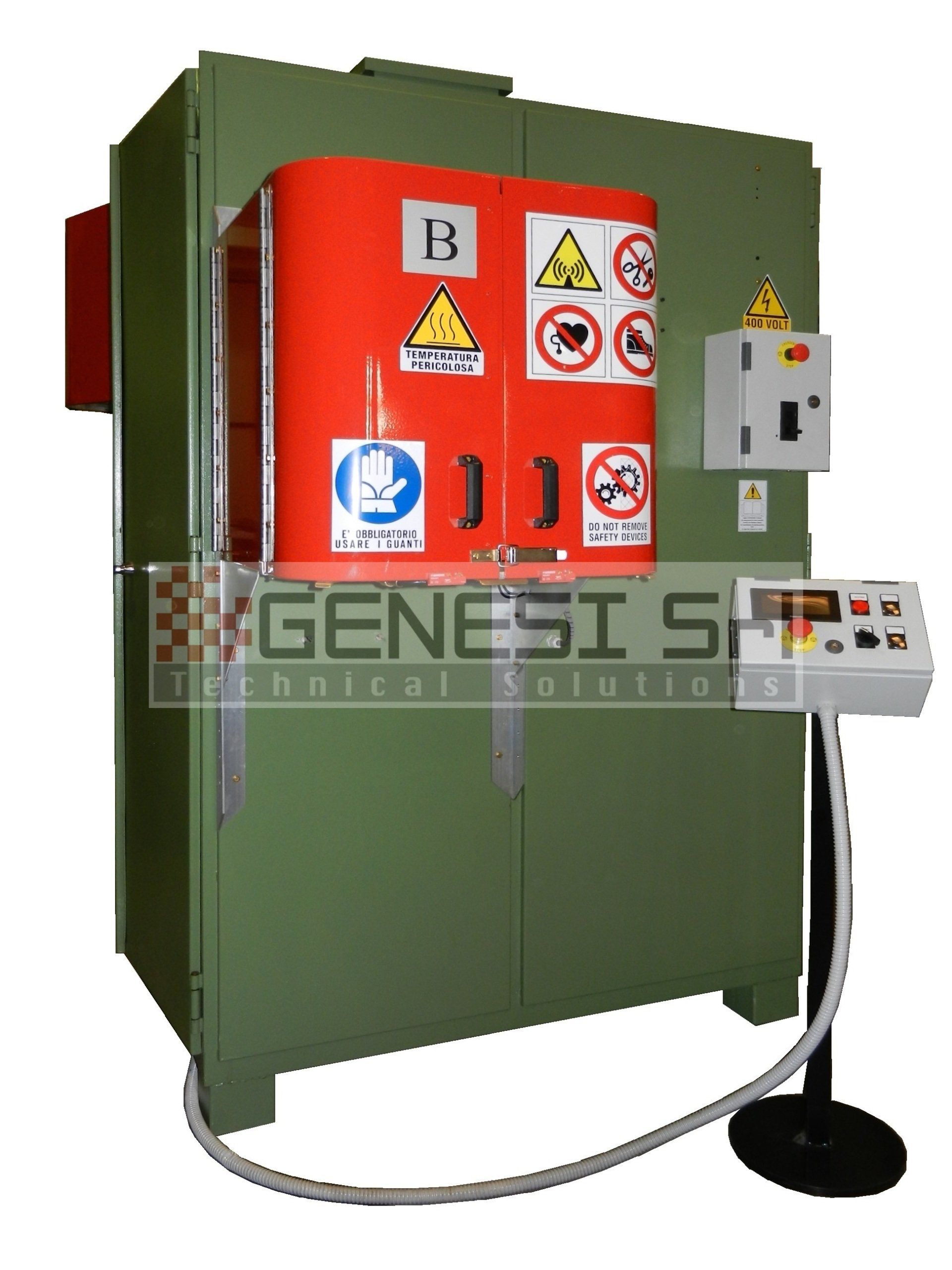
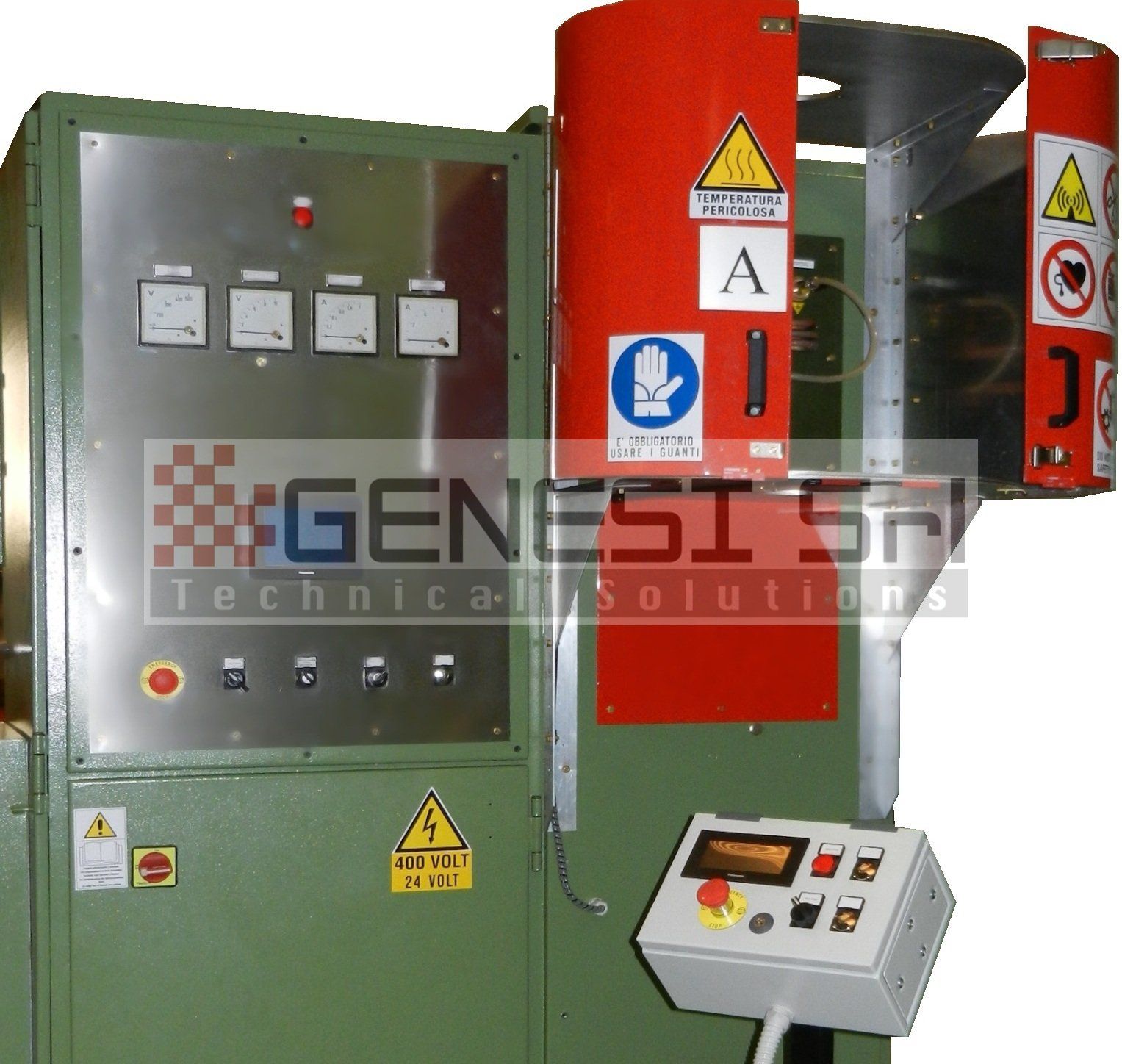
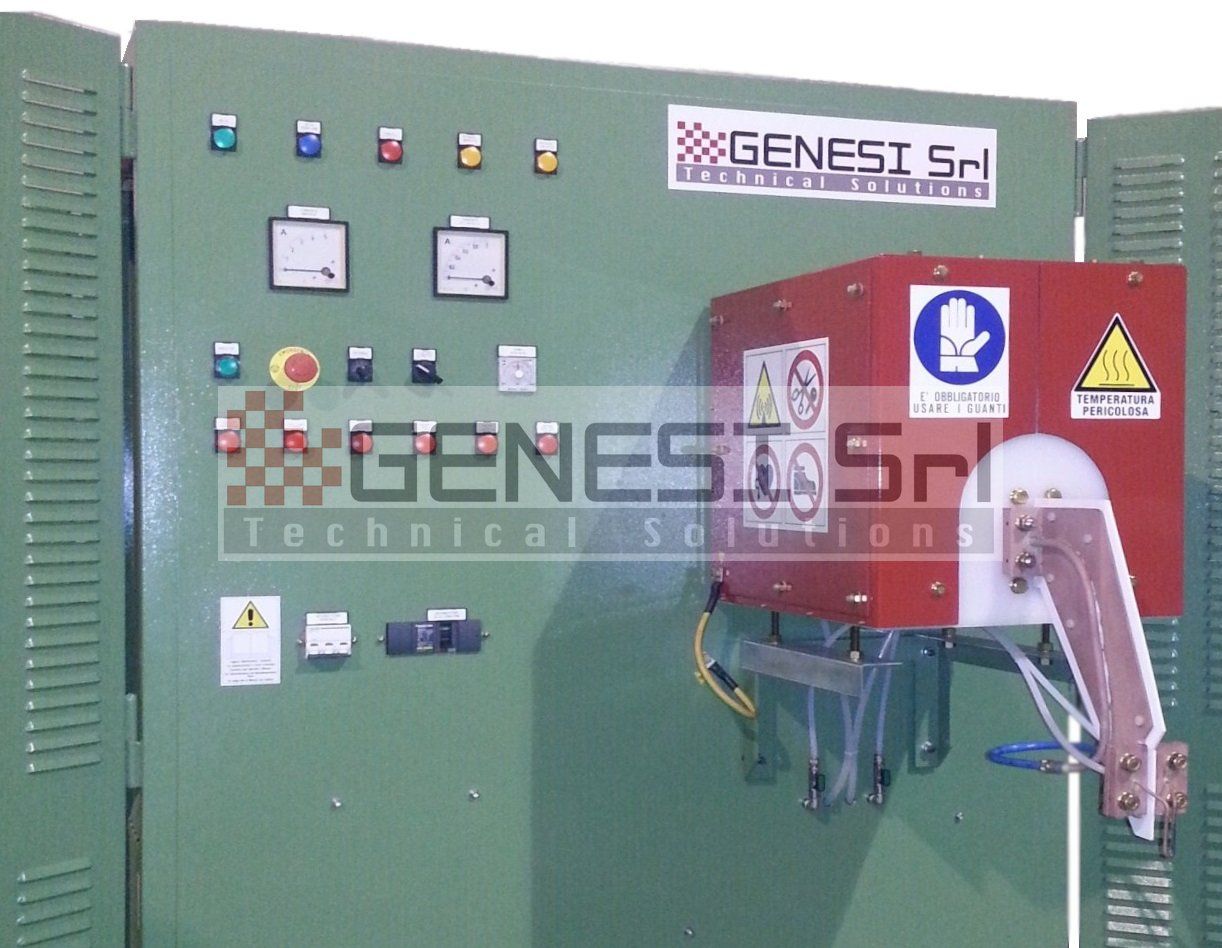
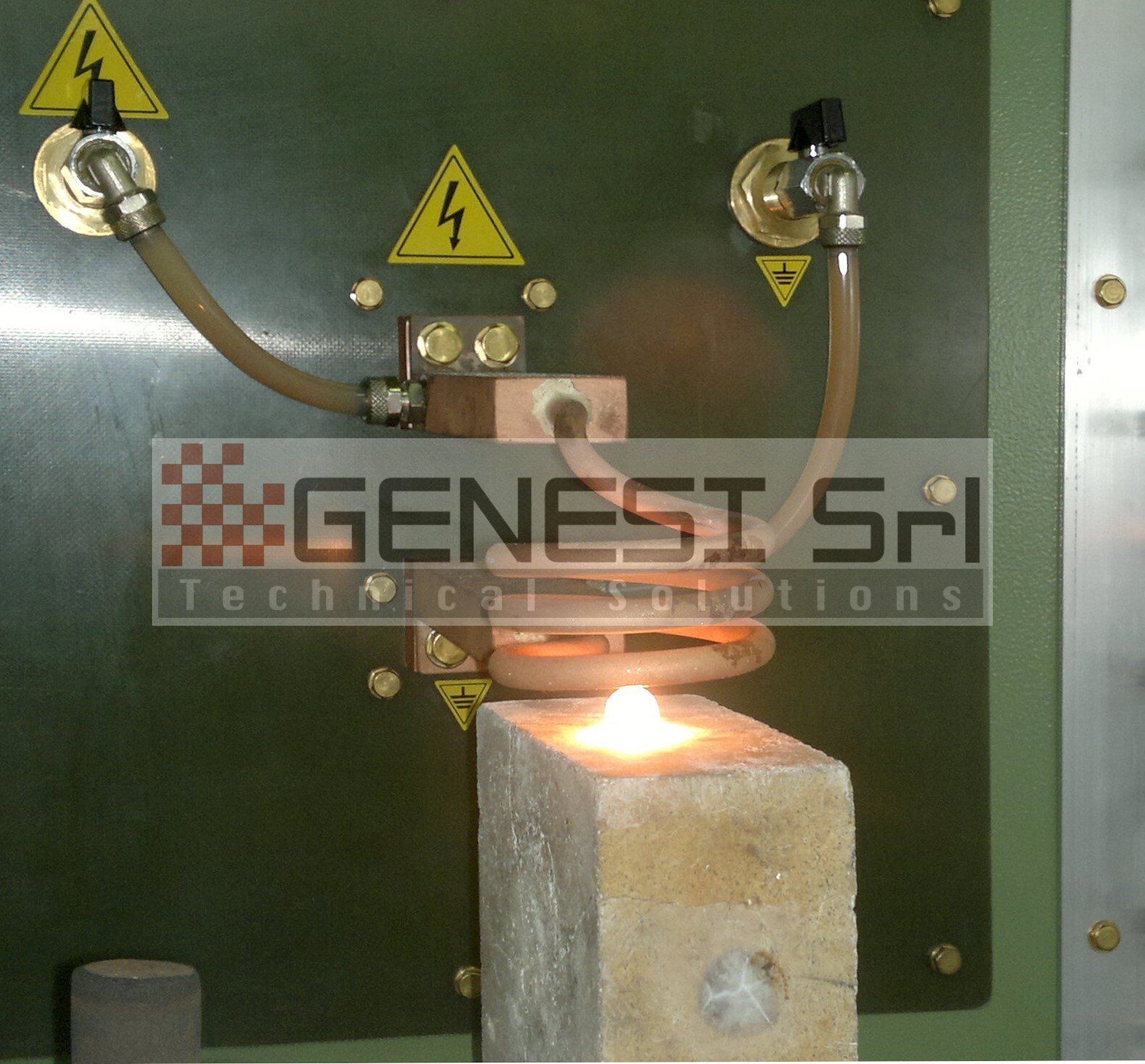
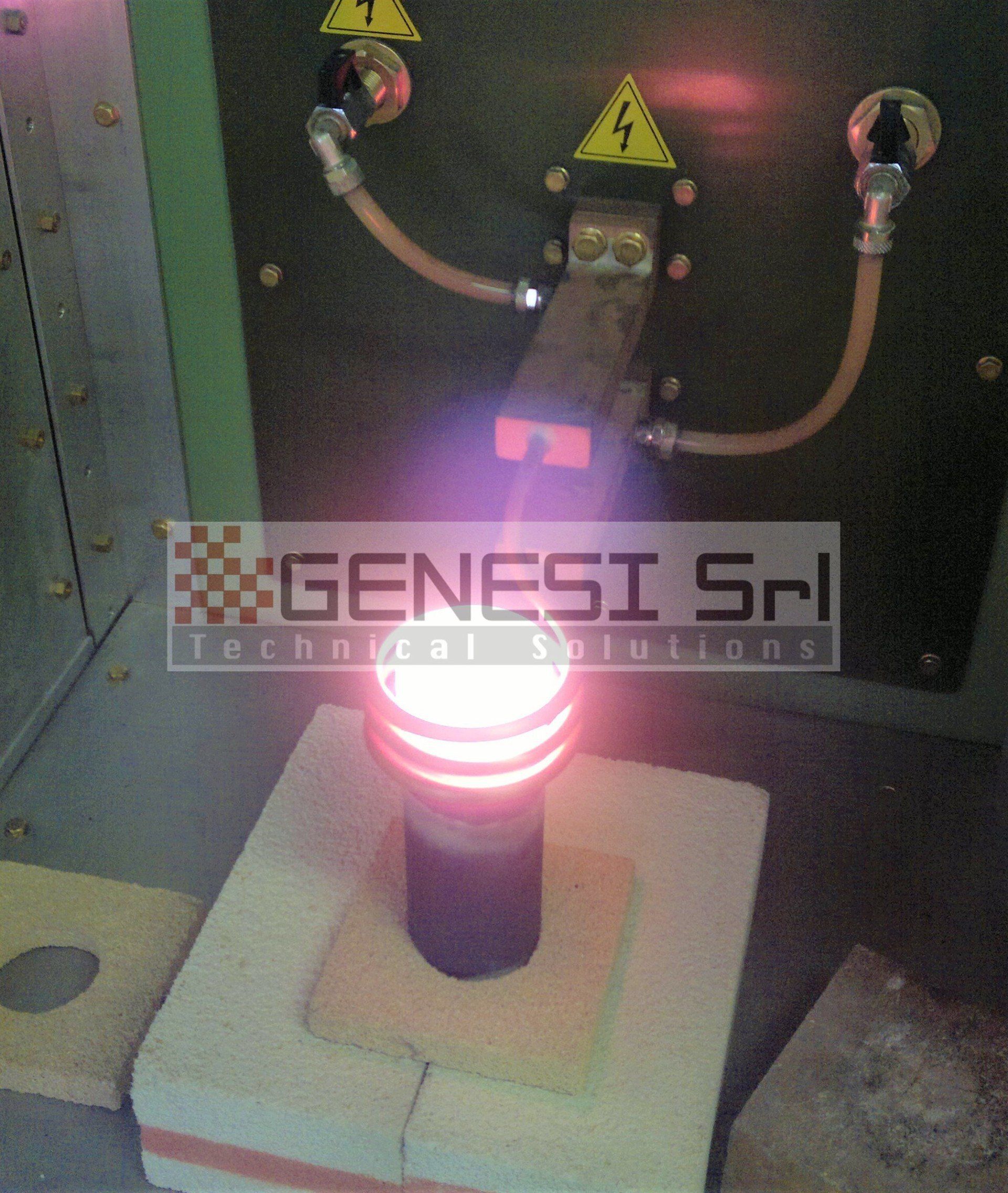
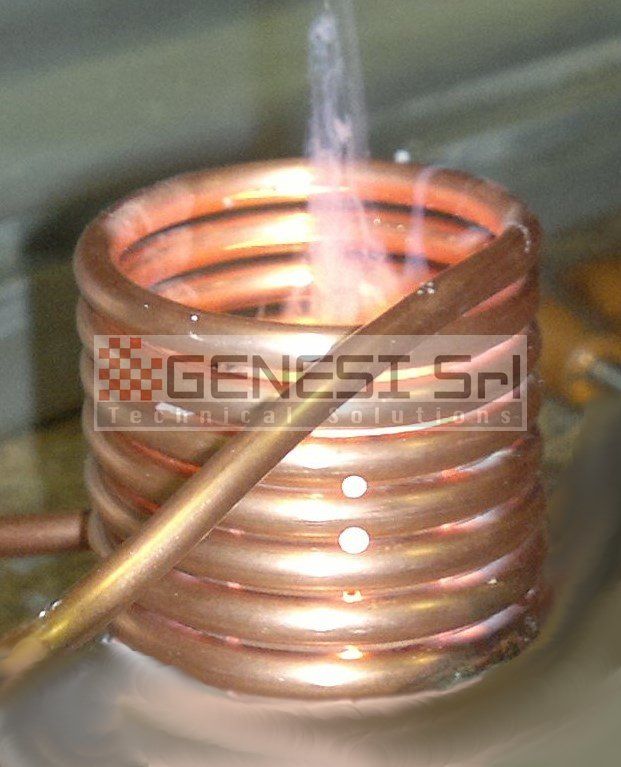
The basic components of an induction heating system are an AC generator, an inductor coil (or “inductor”) and a “load” (i.e. the material to be heated).
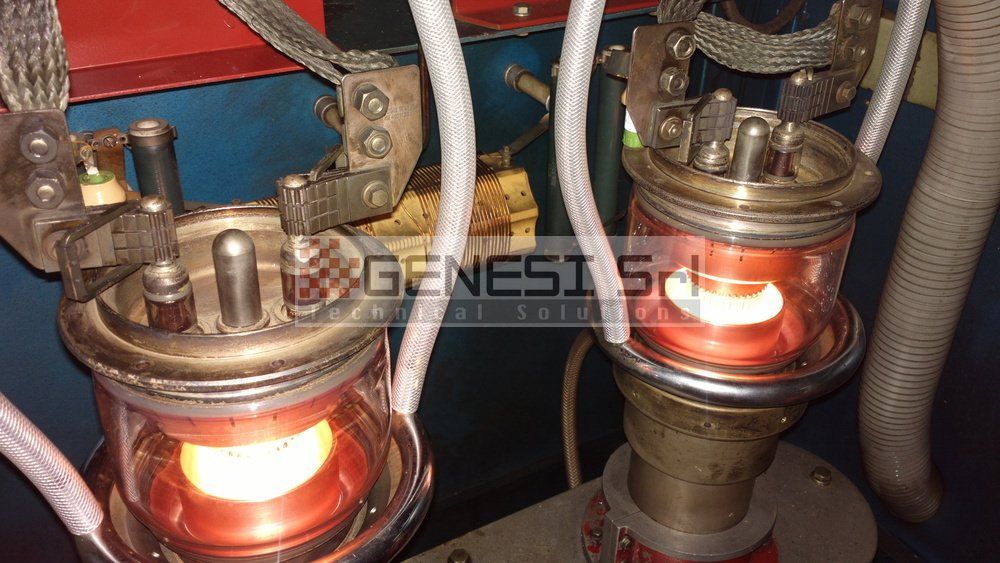
The generator provides the alternating current that flows through the coil, generating a magnetic field around it. When a load is approached, it is carried by eddy currents induced by the magnetic field, which produce a precise, localised and controllable temperature rise in the material, without any physical contact with the coil.
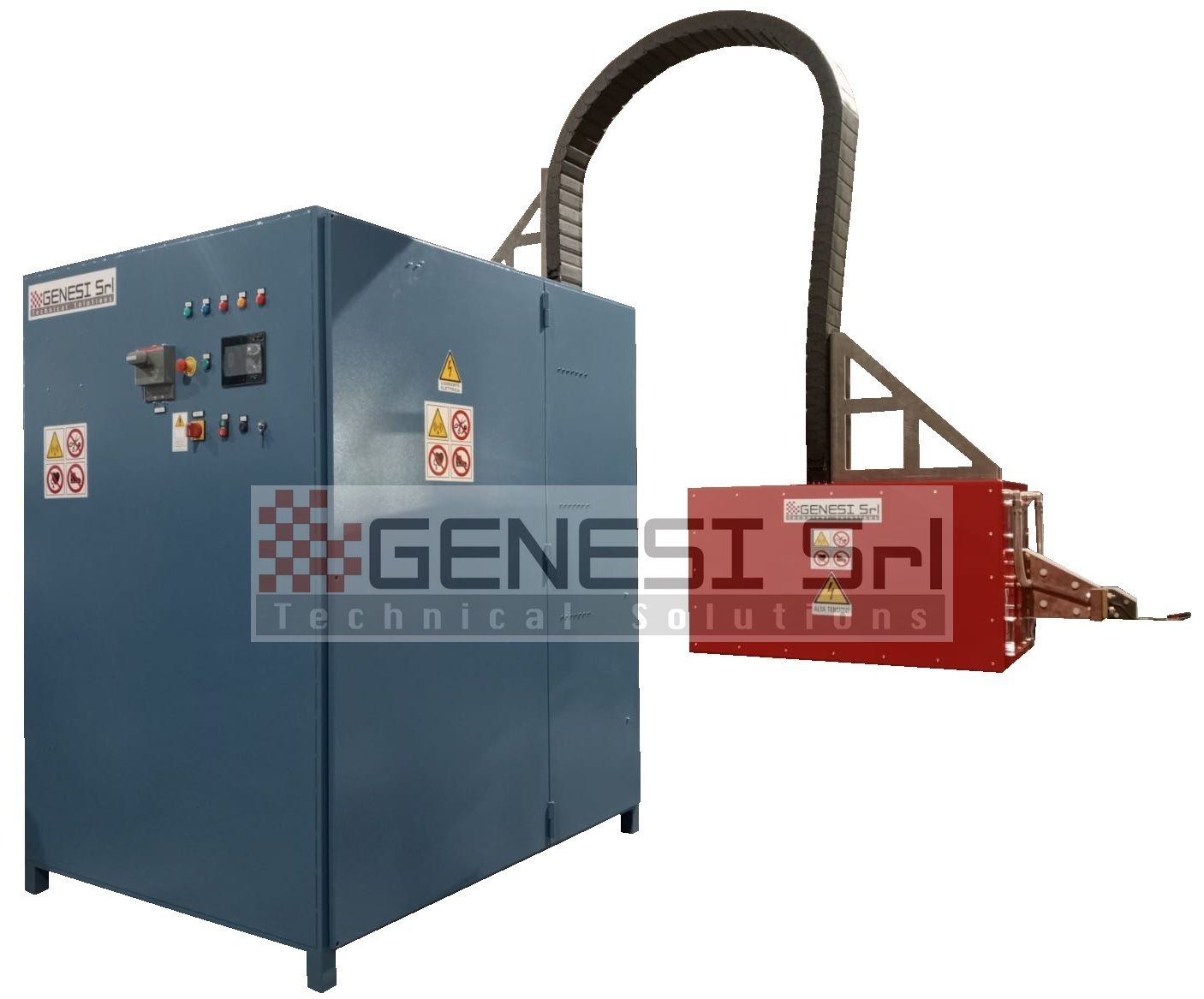
Design and construction of manual and automatic systems for induction heat treatment with power output between 3 and over 100 kW, frequency between 1500 Hz and 1 MHz, specially executed systems for research and development sectors, systems for special heating up to 6 MHz
Execution and installation of remote panels and process controls with the corresponding equipment
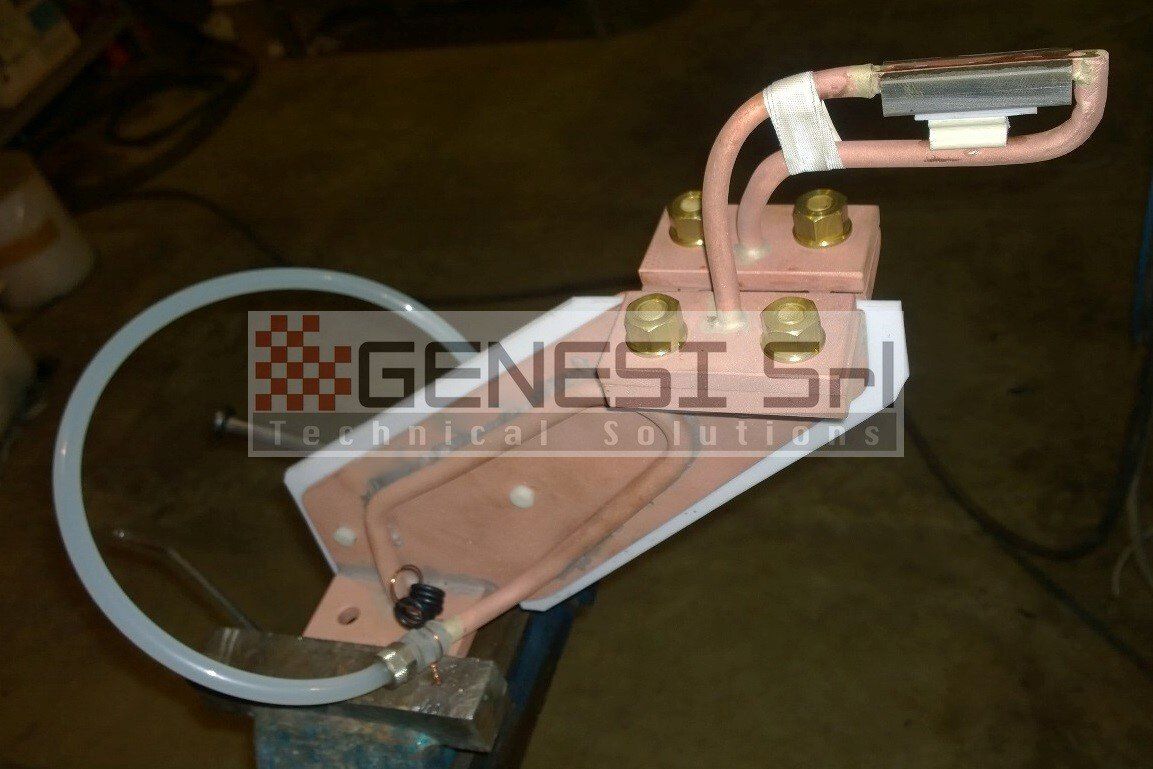
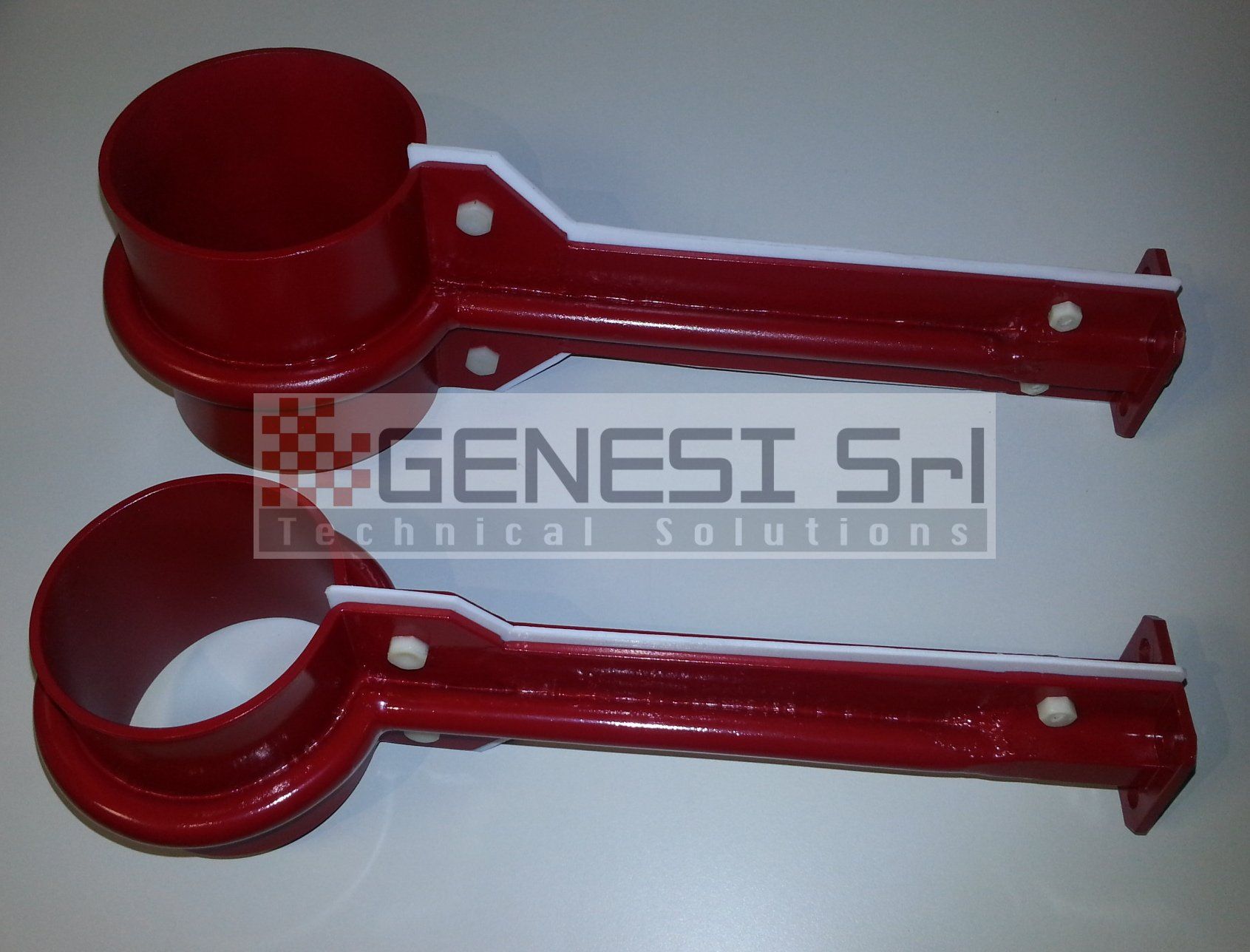
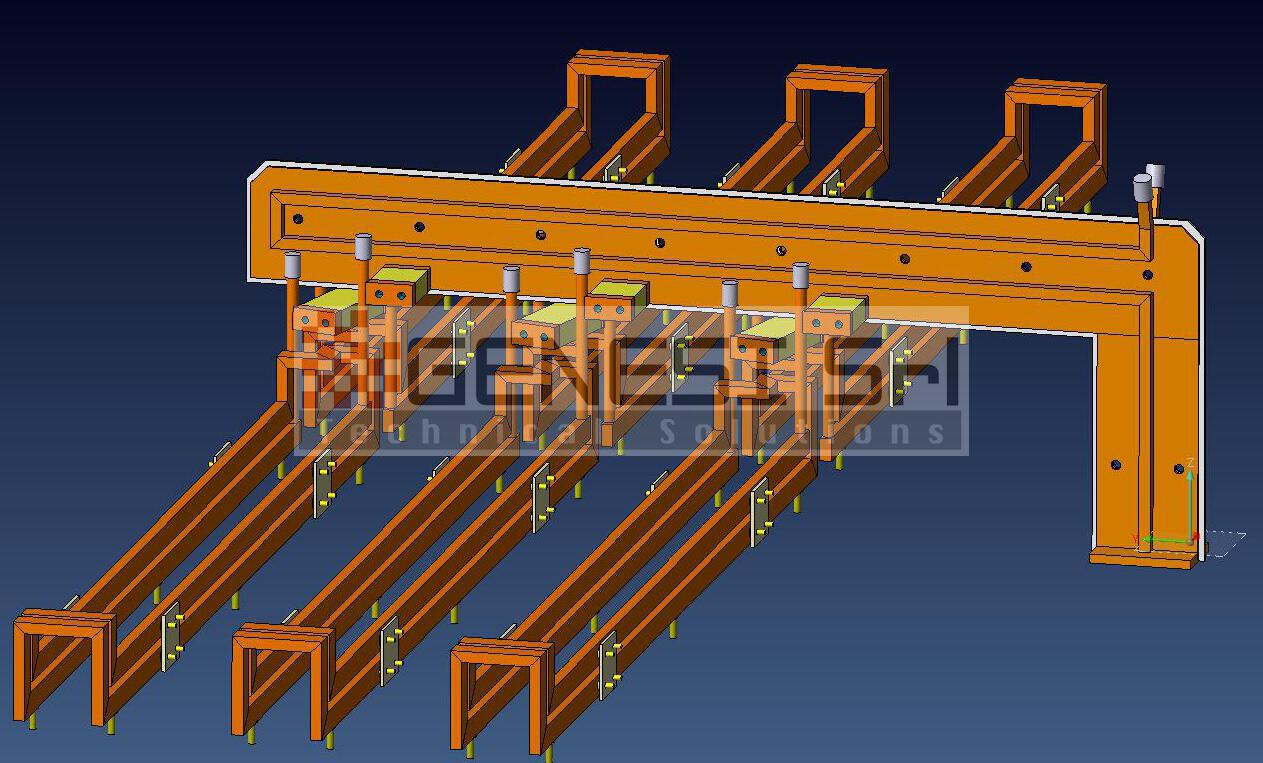
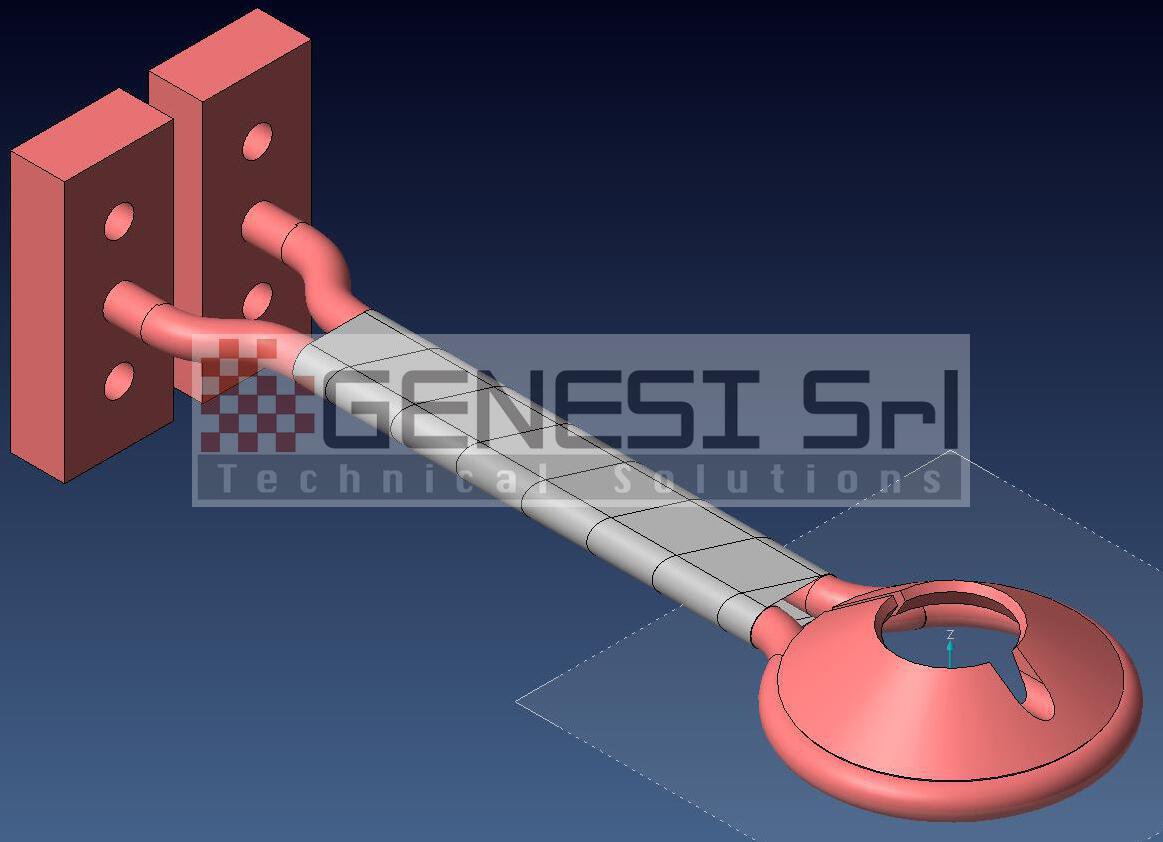
Production of standard and specially executed inductors
Repair and maintenance of existing inductors
Application of optical pyrometers and/or thermocouples
Test and study applications with laboratory for practical tests
Reconditioning of used equipment
Option to interface with Industry 4.0 on request
Consulting and specialised technical support on systems of any make
After-sales technical support with interventions from our staff within 48 hours
Wide range of original and non-original spare parts for systems of any make and year of construction
Most common applications: heating, brazing, welding, tempering, bonding, melting, shrinking, metal joining, annealing, heat treatments etc.